MBA In Healthcare Administration Unleashing Your Potential
MBA In Healthcare Administration opens the door to a dynamic field where business acumen meets medical expertise. This degree is designed for those who aspire to lead and innovate within the healthcare sector, tackling challenges and implementing effective solutions. As the healthcare landscape continues to evolve, understanding the intersection of management and healthcare delivery becomes increasingly vital for future leaders.
In this program, students delve into essential coursework that prepares them for a variety of roles in healthcare management. From understanding the intricacies of healthcare systems to developing strong leadership capabilities, the curriculum equips graduates with the tools necessary to thrive in a competitive job market.
Introduction to MBA in Healthcare Administration
Pursuing an MBA in Healthcare Administration is a significant step for individuals looking to blend their passion for healthcare with leadership and management skills. This specialized program equips students with the essential tools needed to navigate the complex healthcare landscape, making them well-prepared for significant roles within the industry.The core components of an MBA in Healthcare Administration focus on critical areas such as healthcare policy, finance, economics, and operational management.
Students engage in coursework that combines business management principles with healthcare-specific challenges, enabling them to develop strategic thinking and problem-solving skills tailored to the unique requirements of healthcare organizations. Additionally, the program often includes practical experiences through internships or projects that allow students to apply their knowledge in real-world settings, enhancing their learning and professional readiness.
Career Opportunities After Completing the Degree
The career opportunities available to graduates of an MBA in Healthcare Administration are diverse and rewarding. The demand for healthcare professionals with advanced management skills continues to rise, driven by the evolving nature of healthcare delivery systems. Positions that graduates typically pursue include:
- Healthcare Manager: Overseeing operations in hospitals, clinics, or other healthcare facilities, ensuring efficient service delivery and compliance with regulations.
- Healthcare Consultant: Advising healthcare organizations on improving performance, reducing costs, and implementing best practices.
- Healthcare Financial Analyst: Analyzing financial data to assist healthcare organizations in making informed financial decisions and strategic investments.
- Policy Analyst: Working with government agencies or non-profit organizations to analyze and develop policies that impact healthcare delivery and access.
- Practice Manager: Managing day-to-day operations in medical practices, including staffing, budgeting, and patient relations.
Each of these roles plays a critical part in enhancing healthcare delivery and ensuring that organizations can effectively meet the needs of patients and communities. The skills acquired during an MBA in Healthcare Administration—such as strategic planning, leadership, and analytical thinking—position graduates to make a meaningful impact in the healthcare sector.
“Healthcare is not just about treating disease; it’s about understanding the business of health and creating systems that work for everyone.”
Curriculum and Coursework
The curriculum of an MBA in Healthcare Administration is meticulously designed to equip students with the skills and knowledge necessary to thrive in the complex healthcare environment. The diverse coursework not only covers essential management principles but also emphasizes the unique challenges faced by healthcare organizations today.Core courses in an MBA program typically include a blend of business administration fundamentals and specialized healthcare topics.
This combination provides a comprehensive understanding of both the operational and strategic aspects of healthcare management.
Essential Courses in MBA Healthcare Administration
The following courses are commonly found in the MBA in Healthcare Administration curriculum, each addressing critical competencies required in the field:
- Healthcare Management: This course focuses on the principles of managing healthcare facilities, including strategic planning, budgeting, and HR management specific to healthcare.
- Healthcare Policy and Economics: Understanding the impact of policy-making on healthcare delivery and the economic principles that drive healthcare decisions is crucial.
- Health Informatics: This course covers the use of information technology in healthcare, including electronic health records and data management systems.
- Quality Improvement in Healthcare: Students learn frameworks for improving patient care quality and safety through systematic evaluation and change.
- Healthcare Law and Ethics: It’s essential to understand the legal and ethical considerations in healthcare to ensure compliance and ethical decision-making.
Comparison of MBA Healthcare Programs
When selecting an MBA program in Healthcare Administration, it’s beneficial to compare various programs based on unique features they offer. The table below highlights some of the distinct characteristics of popular programs:
| Program | Duration | Specializations | Delivery Mode | Unique Features |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| University A | 2 Years | Health Policy, Informatics | Online/On-campus | Internship opportunities with local hospitals |
| University B | 1 Year | Global Health, Finance | Full-time | Capstone project with a healthcare organization |
| University C | 2 Years | Leadership, Management | Hybrid | Guest lectures from industry leaders |
Elective Courses Enhancing Healthcare Management Skills
Electives play a significant role in tailoring the MBA experience to align with individual career goals. Students often choose electives that augment their expertise in specific areas of healthcare management. Some noteworthy elective courses include:
- Healthcare Marketing: This course teaches strategies for effectively marketing healthcare services to improve patient engagement.
- Data Analytics in Healthcare: Students explore how data analysis can drive decision-making and improve operational efficiency.
- Change Management: Managing change is vital in healthcare settings; this course prepares students to lead transformations within organizations.
- Patient Safety and Risk Management: Understanding how to mitigate risks and enhance patient safety is essential for healthcare leaders.
“The key to success in healthcare management is a blend of strong leadership and deep understanding of the healthcare system.”
Skills Developed through the Program
The MBA in Healthcare Administration equips students with a diverse set of skills necessary for effective management and leadership within the healthcare sector. These skills range from analytical capabilities to interpersonal communication, all aimed at improving efficiency and patient outcomes in healthcare organizations.Leadership and management skills are critical in the healthcare field, as they help professionals navigate the complexities of healthcare systems, foster teamwork, and drive organizational change.
With an ever-evolving landscape influenced by technological advancements and regulatory changes, strong leadership is essential for guiding teams and implementing strategic initiatives.
Key Skills Acquired
During the MBA program, students cultivate both soft and hard skills, which are vital for success in healthcare administration. These skills are essential for addressing challenges and enhancing the quality of care provided to patients.
- Analytical Skills: The ability to assess data and make informed decisions is crucial in optimizing operations and improving patient outcomes.
- Financial Acumen: Understanding financial management, budgeting, and economic principles is necessary for ensuring sustainability and fiscal responsibility within healthcare organizations.
- Strategic Planning: Skills in developing long-term strategies help in setting goals and aligning resources effectively to achieve organizational objectives.
- Regulatory Knowledge: Familiarity with healthcare laws and regulations ensures compliance and minimizes risks associated with non-adherence.
- Interpersonal Communication: Effective communication with healthcare teams, patients, and stakeholders is essential for fostering collaboration and trust.
- Leadership Skills: The capacity to inspire and guide teams through change while maintaining morale is fundamental to successful management in healthcare settings.
Soft and Hard Skills Essential for Success
A well-rounded skill set is vital for thriving in healthcare administration. The following list Artikels key soft and hard skills necessary for effective practice in this field:
- Soft Skills:
- Empathy: Understanding patients’ needs and perspectives enhances patient care and satisfaction.
- Teamwork: Collaboration with diverse healthcare professionals leads to improved patient outcomes.
- Conflict Resolution: Navigating disputes and challenges smoothly maintains a positive workplace environment.
- Adaptability: The ability to adjust strategies and practices in response to the dynamic healthcare landscape is essential.
- Hard Skills:
- Data Analysis: Proficiency in using data analytics tools to interpret healthcare data for decision-making.
- Health Information Technology: Familiarity with electronic health records (EHR) and other digital tools enhances operational efficiency.
- Project Management: Skills in managing projects effectively ensure timely implementation of initiatives and resource allocation.
- Quality Assurance: Knowledge in quality control processes maintains high standards in patient care services.
Benefits of an MBA in Healthcare Administration

Source: clearadmit.com
An MBA in Healthcare Administration offers numerous advantages for professionals looking to elevate their careers in the increasingly complex field of healthcare. This degree not only prepares graduates for leadership roles but also equips them with the necessary tools to navigate the landscape of healthcare management effectively. The value of an MBA in this field is particularly evident when considering career advancement opportunities.
Graduates often find themselves with a competitive edge in a crowded job market, leading to roles that require a blend of business acumen and healthcare expertise. The skills acquired during the program enable individuals to approach healthcare challenges with innovative solutions, making them attractive candidates for leadership positions.
Impact on Salary Expectations and Job Market Competitiveness
The financial benefits associated with obtaining an MBA in Healthcare Administration are substantial. Graduates typically see an increase in their salary expectations compared to their peers without the degree. The following points illustrate the economic advantages of this advanced degree:
- Increased earning potential: According to a survey by the Graduate Management Admission Council, MBA graduates can expect a salary boost of 50% or more compared to their pre-MBA salaries.
- Job market advantage: Health organizations prioritize candidates with advanced business training, resulting in a higher likelihood of securing management roles.
- Diverse career opportunities: An MBA opens doors to various positions such as healthcare consultant, hospital administrator, and health services manager, often leading to roles with higher salaries and greater responsibilities.
- Networking opportunities: MBA programs often provide access to a vast network of professionals and alumni, which can lead to job referrals and partnerships, enhancing career prospects.
“The decision to pursue an MBA in Healthcare Administration was transformative for my career. The knowledge I gained not only enabled me to climb the corporate ladder but also significantly increased my salary. It was the best investment I could have made.”
Sarah L., Healthcare Administrator
Case Studies of Successful MBA Graduates
Many professionals have experienced significant career growth after earning their MBA in Healthcare Administration. For example, John D., who worked as a clinical coordinator, transitioned into a senior management role at a leading hospital shortly after completing his MBA. He credits the program’s focus on strategic management and healthcare policies for his rapid advancement.Another case is Emily R., who leveraged her MBA to shift from a nursing background into healthcare consulting.
She reports that the MBA not only enhanced her understanding of the business side of healthcare but also doubled her earning potential within two years of graduation.These examples highlight how an MBA can serve as a catalyst for career advancement, financial growth, and professional development within the healthcare industry.
Challenges in Healthcare Administration
Healthcare administration is a dynamic field that presents a unique set of challenges. As overseers of healthcare facilities and systems, healthcare administrators must navigate the complexities of patient care, regulatory compliance, and financial management. These challenges can significantly impact the quality of care delivered and the efficiency of operations within healthcare organizations.Healthcare administrators encounter various challenges that can hinder their effectiveness in managing healthcare operations.
These issues range from adapting to rapid technological changes to addressing workforce shortages, all while ensuring that patient care standards are maintained. The following are common challenges faced in healthcare administration along with strategies to mitigate them.
Workforce Management
One of the foremost challenges in healthcare administration is managing a diverse and often strained workforce. The healthcare sector frequently faces staffing shortages and high turnover rates due to factors such as burnout and job dissatisfaction. To combat this, administrators can implement several strategies:
- Invest in employee wellness programs that promote mental health and work-life balance to reduce burnout.
- Create a culture of open communication where staff feel valued and heard, leading to increased job satisfaction.
- Utilize flexible scheduling and telehealth options to accommodate diverse staff needs and attract a broader talent pool.
For instance, many hospitals have adopted initiatives to improve employee engagement, which has led to lower turnover rates and improved patient care outcomes.
Regulatory Compliance
The ever-evolving landscape of healthcare regulations presents another significant challenge. Compliance with laws such as HIPAA and the Affordable Care Act requires administrators to stay informed about legislative changes and adapt their policies accordingly. Strategies for effective compliance management include:
- Regular staff training on compliance protocols and updates to ensure everyone is informed.
- Investing in compliance software that automates monitoring and reporting processes, reducing the risk of human error.
- Establishing a dedicated compliance officer to oversee adherence to regulations and facilitate audits.
For example, a mid-sized hospital implemented a compliance training program that resulted in a 30% reduction in compliance violations within a year.
Financial Management
Financial constraints are a persistent challenge in healthcare administration, particularly with rising operational costs and shrinking reimbursements. To navigate these hurdles, administrators can focus on:
- Implementing cost-control measures, such as optimizing resource utilization and reducing waste.
- Exploring alternative revenue streams, like telehealth services, to enhance financial stability.
- Conducting regular financial audits to identify areas for improvement and ensure accurate budgeting.
A healthcare organization that adopted a robust financial management system saw a significant improvement in its bottom line, enabling it to invest in new technologies and staff training.
Technology Integration
The rapid advancement of technology in healthcare poses both opportunities and challenges. Integrating new systems, such as Electronic Health Records (EHR), can be daunting but is essential for improving patient care. Administrators can address this challenge by:
- Providing comprehensive training for staff to facilitate smooth transitions to new technologies.
- Engaging stakeholders early in the decision-making process to ensure buy-in and address concerns.
- Regularly assessing technology effectiveness and making adjustments based on user feedback.
For instance, a healthcare facility that invested in comprehensive training for its EHR system reported increased efficiency and enhanced patient data accessibility, illustrating the importance of effective technology integration.
Networking and Professional Development
Building a robust network and focusing on professional development are pivotal components of a successful career in healthcare administration. The healthcare sector is a dynamic field that thrives on relationships, collaborations, and knowledge sharing. Engaging with industry professionals can open doors to new opportunities, provide invaluable insights, and enhance your career trajectory.Networking in the healthcare industry is crucial for several reasons.
It fosters connections that can lead to mentorship opportunities, partnerships, and collaborations that can enhance your knowledge and skills. Networking provides access to insider information on job openings, trends, and best practices. Additionally, it allows you to build a support system of peers who understand the unique challenges of the healthcare landscape.
Engaging with Professional Organizations and Associations
Joining professional organizations is an effective way to engage with the healthcare community. These organizations provide platforms for networking, professional development, and advocacy for the industry. Active participation can lead to leadership opportunities and enhance your resume.Consider these strategies to engage with professional organizations:
- Attend local chapter meetings to meet fellow members and industry leaders.
- Participate in webinars and training sessions offered by the organizations.
- Volunteer for committees or task forces to contribute to industry initiatives.
- Utilize online platforms and forums to connect with members globally.
Conferences and Events for MBA Graduates in Healthcare Administration
Attending industry conferences and events is a beneficial way to stay updated on emerging trends and network with professionals. These gatherings offer a wealth of knowledge through keynote speeches, breakout sessions, and networking opportunities. Here’s a list of notable conferences that MBA graduates in healthcare administration should consider:
- Healthcare Information and Management Systems Society (HIMSS) Global Conference & Exhibition
- American College of Healthcare Executives (ACHE) Congress on Healthcare Leadership
- National Association of Healthcare Access Management (NAHAM) Annual Conference
- Healthcare Financial Management Association (HFMA) Annual Conference
- Institute for Healthcare Improvement (IHI) National Forum on Quality Improvement in Health Care
Attending these events not only enhances your knowledge but also provides opportunities to meet industry leaders, exchange ideas, and establish collaborative relationships. Each event typically features a mix of educational sessions, networking opportunities, and exhibitions that create an immersive experience for attendees.
“Networking is not about just collecting contacts; it’s about planting relations.”
Future Trends in Healthcare Administration
The landscape of healthcare administration is evolving rapidly, driven by technological advancements, regulatory changes, and shifts in patient expectations. Understanding these future trends is critical for professionals who aim to lead in this dynamic environment. As healthcare systems adapt to new challenges and opportunities, the focus will increasingly be on innovation, efficiency, and improved patient care.As we move forward, several emerging trends are set to reshape healthcare administration, making it essential for leaders to stay informed and agile.
Technology and innovation play pivotal roles in this transformation, influencing everything from how care is delivered to how organizations operate on a structural level. The following sections highlight key trends and their implications for the future of healthcare management.
Emerging Trends Impacting Healthcare Administration
Various trends are influencing the direction of healthcare administration, and understanding these can help organizations navigate upcoming challenges effectively. Here are some key trends to consider:
- Telehealth Expansion: The COVID-19 pandemic accelerated the adoption of telehealth services. Remote consultations have become commonplace, making healthcare more accessible while reducing overhead costs.
- Value-Based Care Models: There’s a growing shift from fee-for-service to value-based care, which emphasizes patient outcomes and efficiency, promoting better care at lower costs.
- Data Analytics and AI: Leveraging big data and artificial intelligence for predictive analytics is becoming crucial. These technologies help identify trends, improve patient outcomes, and streamline operations.
- Patient-Centric Approaches: A focus on patient experience is gaining traction, with healthcare providers prioritizing personalized care and enhancing patient engagement strategies.
- Interdisciplinary Collaboration: The importance of collaborative care models is increasing, where healthcare professionals from various disciplines work together to provide comprehensive care solutions.
The Role of Technology and Innovation
Technology and innovation are at the forefront of transforming healthcare administration, impacting various aspects of the field. The integration of new technologies is not just a trend; it is a necessity for improving operational efficiency and patient care quality. Here are specific areas where technology is making significant inroads:
- Electronic Health Records (EHR): EHR systems are becoming more sophisticated, allowing for better data sharing and seamless communication among healthcare providers.
- Wearable Health Devices: These devices enable continuous patient monitoring, leading to timely interventions and proactive health management.
- Blockchain Technology: This technology promises enhanced data security and integrity, particularly in managing patient records and ensuring compliance with regulations.
- Robotic Process Automation (RPA): RPA is streamlining administrative processes, reducing the burden on staff, and minimizing errors in repetitive tasks.
- Telemedicine Platforms: Innovative platforms are emerging that not only facilitate consultations but also provide integrated solutions for continuous care management.
Current and Predicted Trends in Healthcare Management, MBA In Healthcare Administration
To better understand the shifting landscape, it is helpful to examine current trends alongside predicted future ones. The table below illustrates key trends that are currently shaping healthcare administration alongside anticipated developments:
| Current Trends | Predicted Trends |
|---|---|
| Increased use of telehealth services | Widespread implementation of hybrid care models |
| Adoption of electronic health records | Integration of AI for personalized medicine |
| Focus on patient experience | Enhanced predictive analytics for patient care |
| Interdisciplinary care teams | Expansion of collaborative care networks |
| Value-based care models | Shift towards community-based health initiatives |
The future of healthcare administration is poised for significant transformation. Staying ahead of these trends will empower healthcare leaders to navigate the complexities of the industry effectively while delivering high-quality care to patients.
Admission Requirements and Application Process

Source: mbastack.org
The journey toward earning an MBA in Healthcare Administration is an exciting one, filled with opportunities for personal and professional growth. However, before you can embark on this journey, it’s essential to understand the typical admission requirements and the application process that will help you stand out as a candidate.The admission requirements for MBA programs in Healthcare Administration generally include a combination of academic qualifications, professional experience, and personal attributes.
Most programs expect applicants to hold a bachelor’s degree from an accredited institution, with a preferred background in healthcare, business, or related fields. Additionally, many programs require standardized test scores, such as the GMAT or GRE, although some schools may waive this requirement for qualified candidates.
Typical Admission Requirements
Understanding the prerequisites can significantly enhance your chances of acceptance. Here are the common admission requirements:
- Bachelor’s Degree: A degree from an accredited institution is typically required.
- Transcripts: Official academic transcripts from previous educational institutions must be submitted.
- Work Experience: Many programs prefer candidates with relevant professional experience in healthcare or management.
- Standardized Test Scores: GMAT or GRE scores are often required, although waivers may be available.
- Letters of Recommendation: Most schools request two or three letters from professionals who can speak to your qualifications and potential.
- Personal Statement: A compelling personal statement outlining your motivations and career goals is crucial.
- Resume/CV: A current resume detailing your educational background and work experience is also necessary.
Application Process
Navigating the application process requires attention to detail and strategic planning. Begin by researching various programs to align your goals with their offerings. Most schools have an online portal for applications, which simplifies the submission of documents. After preparing your materials, follow these steps:
- Complete the Application Form: Fill out the online application accurately and thoroughly.
- Submit Transcripts: Ensure all academic records are sent directly from your previous institutions.
- Prepare Test Scores: Arrange for your standardized test scores to be sent to the schools you’re applying to.
- Gather Recommendations: Approach recommenders early and provide them with any necessary information to help them write strong letters.
- Craft Your Personal Statement: Write a compelling narrative that highlights your experiences, aspirations, and reasons for pursuing an MBA in Healthcare Administration.
- Review and Submit: Double-check your application for completeness and accuracy before submitting.
Effective Personal Statements and Resumes
A well-crafted personal statement and resume can differentiate you from other candidates. Your personal statement should convey your passion for healthcare and leadership. For example, you might start with a personal anecdote that illustrates your commitment to healthcare, followed by your career goals and how the MBA program aligns with them.Similarly, your resume should not only list your qualifications but also highlight specific achievements.
For instance, rather than stating that you worked as a healthcare manager, elaborate on how you improved patient satisfaction rates by implementing new protocols, showcasing measurable outcomes.
“Your application materials are your chance to tell your story and demonstrate your unique qualifications for the MBA in Healthcare Administration.”
Online vs. On-Campus MBA Programs
The choice between online and on-campus MBA programs in Healthcare Administration is an important decision for prospective students. Each format offers unique advantages and challenges that can significantly impact learning experiences, networking opportunities, and career trajectories. Understanding these differences can help students make informed choices that align with their personal circumstances and professional goals.Comparing the two formats reveals a stark contrast in terms of flexibility, accessibility, and mode of delivery.
Online programs provide the advantage of self-paced learning and the ability to balance education with professional responsibilities. On the other hand, on-campus programs offer face-to-face interaction with faculty and peers, which can enhance collaboration and networking opportunities.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Online and On-Campus Programs
Both online and on-campus MBA programs have specific strengths and limitations, and it’s essential to weigh these factors when making a decision.
- Online Programs:
- Advantages:
- Flexibility in scheduling allows students to manage work and study commitments effectively.
- Accessibility for students who may live far from campus or have mobility challenges.
- The ability to access a diverse range of resources and learning materials online.
- Lower costs associated with commuting and physical materials.
- Disadvantages:
- Less opportunity for in-person networking and relationship building.
- Requires a high level of self-discipline and motivation to stay engaged.
- Some employers may still prefer candidates with traditional on-campus experience.
- Advantages:
- On-Campus Programs:
- Advantages:
- Direct access to faculty for mentorship and support.
- Opportunities for networking with peers and industry professionals during classes and events.
- Structured environment that may enhance focus and commitment to studies.
- Disadvantages:
- Less flexibility in scheduling, requiring a more rigid time commitment.
- Potentially higher costs associated with commuting and campus facilities.
- May not accommodate working professionals who cannot attend classes on a fixed schedule.
- Advantages:
Key Differences Between Online and On-Campus Programs
To clarify the contrasts between online and on-campus MBA programs in Healthcare Administration, the following table summarizes the key differences in areas such as accessibility, learning style, and cost:
| Criteria | Online Programs | On-Campus Programs |
|---|---|---|
| Flexibility | High; students can learn at their own pace and schedule. | Moderate; classes are held at scheduled times requiring attendance. |
| Accessibility | Accessible from anywhere with an internet connection. | Restricted to students who can physically attend the campus. |
| Networking Opportunities | Virtual networking; less direct interaction. | In-person networking events and class interactions. |
| Cost | Typically lower; savings on travel and housing. | Higher; includes commuting and campus-related expenses. |
| Learning Style | Self-directed; requires strong time management skills. | Structured; includes interactive and collaborative learning experiences. |
Choosing the right MBA program format is essential to aligning your educational path with your career aspirations in healthcare administration.
Closure
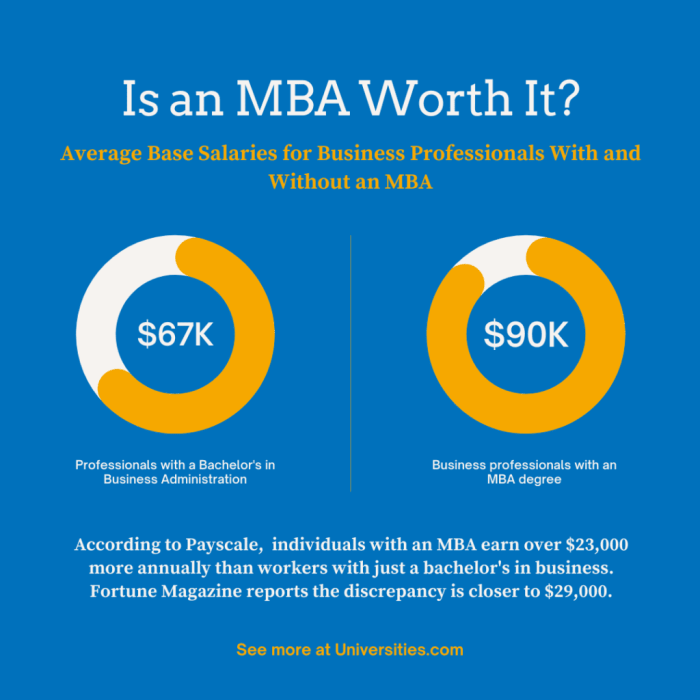
Source: universities.com
In summary, pursuing an MBA In Healthcare Administration not only enhances your career prospects but also empowers you to make a significant impact in the healthcare industry. With the skills gained through this program, graduates are well-positioned to navigate the complexities of healthcare management while driving innovation and improving patient outcomes. As the industry continues to change, the demand for knowledgeable leaders will only grow, making this degree a valuable investment in your future.
Commonly Asked Questions: MBA In Healthcare Administration
What are the typical job roles after completing an MBA in Healthcare Administration?
Graduates can pursue roles such as healthcare manager, healthcare consultant, and hospital administrator, among others.
Is an MBA in Healthcare Administration worth it?
Yes, it often leads to better job prospects, higher salaries, and opportunities for career advancement in the healthcare sector.
Can I complete the program online?
Many universities offer both online and on-campus options, providing flexibility to fit your schedule.
What skills will I gain from this program?
Students develop leadership, analytical, communication, and strategic planning skills essential for effective healthcare management.
How long does it typically take to complete the MBA program?
Most MBA programs can be completed in 1-2 years, depending on whether you study full-time or part-time.